Evaluation of the effectiveness of investment projects is necessary to understand the feasibility
of investments, as
well as to choose the most profitable option for investing funds from various alternatives. Various
indicators are used
to assess the economic efficiency of investments. One such indicator is Net Present Value (NPV).
Let's look at what Net Present Value is, how it is calculated, and where it is used. Net Present
Value is the sum of
discounted net cash flows of a project, i.e. it is future cash flows minus investments. If the Net
Present Value of the
project has a positive value - the project is considered economically profitable, and if the Net
Present Value of the
project has a negative value - the project is not economically profitable.
Let's show by example how to calculate the Net Present Value, but first you need to have an
understanding of what
discounting is.
We all know that the value of money changes over time, it is influenced by various factors, such as
inflation,
alternative investments. Discounting is the basis for calculating the time value of money, that is,
it is a method of
bringing future cash flows to the present time, taking into account compound interest. In order to
calculate the Net
Present Value, it is necessary to determine the correct discount rate.
The discount rate is the required rate of return for the investor, i.e., it is the expected rate of
return that the
investor expects to receive from alternative investments with equal risks. Thus, to calculate the
discount rate, one
must take into account inflation, the risk factor, and the return on risk-free investments. Thus, it
is also necessary
to take into account that, depending on the direction of investments, the Weighted Average Cost of
Capital (WACC) can be
taken as the discount rate.
The Net Present Value is calculated using the following formula:
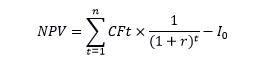
Where:
I0 – Investments
CFt - Cash Flow in the t-period
r - Discount Rate
n - Settlement Period
Table 1 shows an example of a Net Present Value calculation.
Let's assume that the discount rate is 10%, the calculation period is 5 years (project time), the
cash flow of the
project is $12,000 per year, and the investment is $27,000.
Table 1 - Calculation of the Net Present Value of the investment project
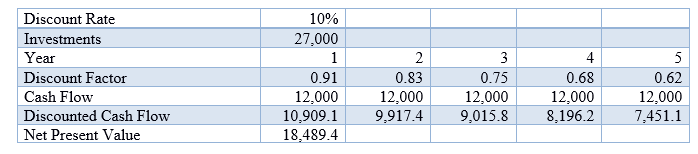
Thus, the Net Present Value of the project will be $18,489.4. Focusing on this indicator, we can say that the investment project is economically profitable, but the practice should also look at other indicators of economic efficiency of investment projects and alternative investments.
